What Animals Live In The Abyssopelagic Zone
Deep-sea CREATURES
Abyssal creatures: what secrets practise the ocean depths hold?
Afterward centuries of enquiry, the species that populate the Earth are well known, at least those that are within our reach. Because at that place are others, nowadays in remote and practically inaccessible places, which are largely unknown. These include those establish in the deep sea. Below, nosotros take a closer await at the abyssal creatures that inhabits the seas and oceans of our planet.
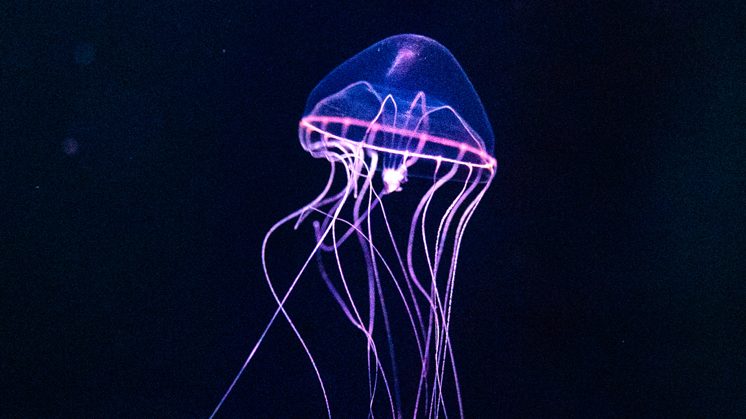

One of the most curious aspects of deep-sea creatures is its bioluminescence
Several hundred metres below sea level, where low-cal cannot penetrate, in that location are thousands of species that have fabricated the deep sea their habitat. If we talk well-nigh the viperfish, the telescope octopus or vampire squid, they probably don't fifty-fifty ring a bong — even if their name makes you call back of monstrous creatures and they may indeed look monstrous — justthese are only three of the thousands of species that, co-ordinate to the Census of Marine Life External link, opens in new window., alive in the deep sea.
External link, opens in new window., alive in the deep sea.
These thousands of species, many of them discovered during the last decades thanks to the Ocean Biodiversity Information System (OBIS) External link, opens in new window., brand upwardly the deep-sea creatures or, in other words, those animals that live beyond the epipelagic zone, i.e. 200 metres below the surface. Although there are many,scientists agree that more than than 80 % of the ocean flooring has not all the same been surveyed with modern applied science, then the secrets of the deep ocean have only just begun to exist revealed.
External link, opens in new window., brand upwardly the deep-sea creatures or, in other words, those animals that live beyond the epipelagic zone, i.e. 200 metres below the surface. Although there are many,scientists agree that more than than 80 % of the ocean flooring has not all the same been surveyed with modern applied science, then the secrets of the deep ocean have only just begun to exist revealed.
WHAT IS THE Deep-sea ZONE
The abyssal zone, likewise known equally the abyssopelagic zone, is one of the levels into which the oceans are divided and it is found between three,000 and 6,000 metres below the surface. In fact, the discussion abyssal comes from the Latin abyssalis, pregnant completeness, something bottomless or extremely deep. Nevertheless, abyssal fauna expands across this surface area. In fact, from a zoological bespeak of view, abyssal creatures is considered to be all the fauna that lives below a depth of 200 metres, every bit few species are capable of living beyond i,000 metres.
Characteristics of the abyssal zone
The abyssal zone, due to its depth, is an extremely demanding surroundings for living beings:it is an aphotic region, i.e. it lacks lite; the temperature ranges between 0 ºC and three ºC; there is a shortage of nutrients, which makes it hard for the species that inhabit it to feed and abound; and the hydrostatic pressure increases with depth, for example, in the Challenger Deep, the deepest point of the ocean at almost 11,000 metres, the pressure level is a one thousand times higher than at sea level.
What is the abyssal plain
The deep-sea apparently is a practically flat strip of state typical of the abyssopelagic zone that extends beyond the continental shelf, the continental barrier and the continental rising.It makes up about 50 % of the ocean flooring and below it we would only notice the oceanic trenches, that can reach a depth of eleven,000 metres — such as the Challenger Deep, mentioned above, which is located at the southern finish of the Mariana Trench. Light does not reach the manifestly, then it harbours piddling life, mainly chemosynthetic bacteria, some invertebrates (worms) and some vertebrates (fish).
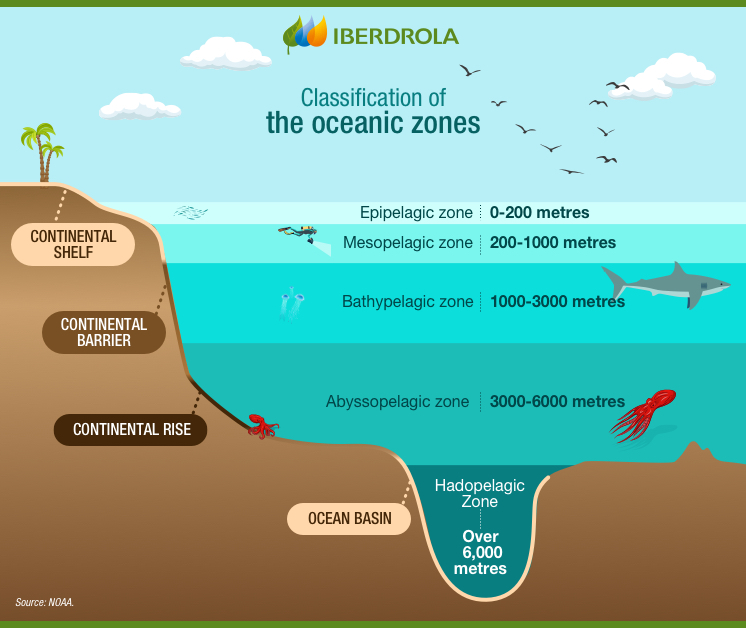
Classification of the oceanic zones.
Come across INFOGRAPHIC: Classification of the oceanic zones [PDF]
ABYSSAL ANIMALS
E'er since the British regime launched the Challenger expedition in 1872 to map the deep ocean, discovering forty new species, there have been numerous scientific voyages that have gradually unravelled a small percentage of its mysteries.The expeditions past the enquiry teams of the US National Oceanic and Atmospheric Assistants (NOAA) or those by the aforementioned OBIS are a adept example of this.
In 2018, an Australian trek discovered more 100 species of abyssal fish at a depth of four,800 metres, some of them faceless, i.e. without visible eyes or mouths, others terrifying, such every bit the lizardfish with a huge mouth, photos of which went viral.Their advent is justified past their harsh living conditions, as they accept had to conform to the surroundings in guild to survive, and this gives them a very special ready of attributes: soft bodies, transparent skins, sharp teeth, underdeveloped eyes, extendable stomachs, etc.
If there is one feature that stands out above all others, information technology is bioluminescence. This phenomenon, which occurs in 90 % of the animals living in the deep sea, allows them to create light througha chemical reaction, which they use for defence, to locate food or as a lure for reproduction. Bioluminescence tin exist diffuse, localised or appear in specialised organs.
Hither are some examples of the amazing abyssal creatures:
Abyssal fish
- Caulophrynidae: are characterised by a peduncle to a higher place the rima oris with a luminous organ at the tip, which they use for hunting. Living on the abyssal bottom, they detect it hard to discover a mate, and then the larger female hosts the male.
- Chauliodus danae: the viperfish has disproportionately large and very sharp teeth that allow it to kill its prey. Males tin can grow upward to xv centimetres long. The chauliodus sloani, in the same family and larger in size, inhabits waters upward to 4,000 metres deep.
- Saccopharynx: similar to eels, they take extensible stomachs, large jaws — hence their nickname of gulper eels — and a bulb-shaped luminous organ in the tail. They live at depths of around ii,000 metres and tin can reach up to two metres in length.
Abyssal crustaceans and deep-sea molluscs
- Colossendeis: this genus of marine spiders, some of which are bioluminescent, lives in deep water and is notable for the length of their limbs, which tin reach 40-50 centimetres, in contrast to their pocket-sized bodies.
- Vampyroteuthis infernalis: known as the vampire squid, it is capable of living in the aphotic depths and lacks an ink reservoir, instead releasing a viscid cloud of bioluminescent mucus to scare off predators.
- Amphitretus pelagicus: native to the abyssal zone, the telescope octopus inhabits the tropical and subtropical waters of the Indian and Pacific Oceans, and is distinguished from other octopus species by its translucent, tubular eyes.
Source: https://www.iberdrola.com/sustainability/abyssal-creatures
Posted by: winklerwhadminvabot.blogspot.com

0 Response to "What Animals Live In The Abyssopelagic Zone"
Post a Comment