During Which Geologic Period Did Plants And Animals First Appear In Land Environments?
Paleozoic Era: Facts & Information
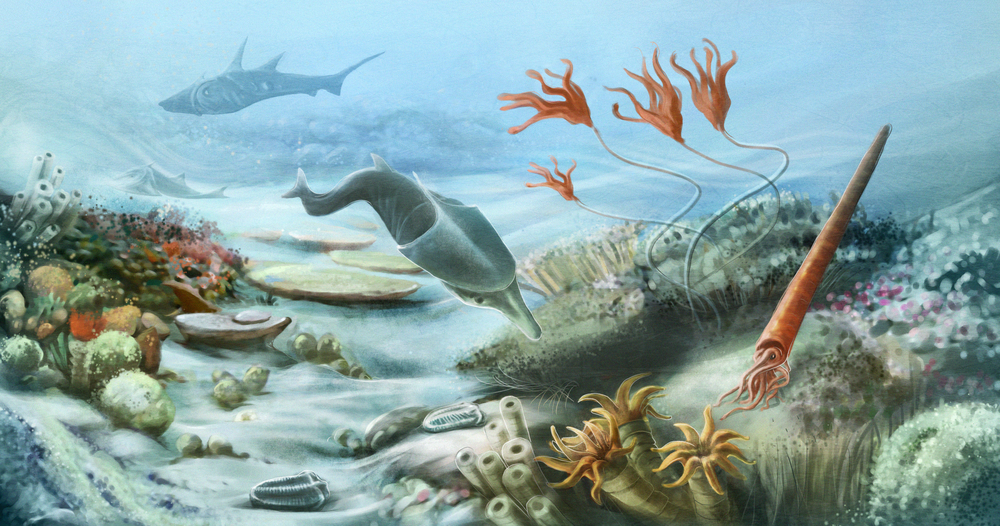

The Paleozoic Era, which ran from 541 million to 251.9 million years ago, was a time of great modify on World. The era began with the breakup of one supercontinent and the germination of some other. Plants became widespread. And the commencement vertebrate animals colonized land.
Life in the Paleozoic
The Paleozoic began with the Cambrian Period, 53 million years best known for ushering in an explosion of life on Earth. This "Cambrian explosion" included the evolution of arthropods (ancestors of today's insects and crustaceans) and chordates (animals with rudimentary spinal cords).
In the Paleozoic Era, life flourished in the seas. Later on the Cambrian Period came the 45-meg-year Ordovician Catamenia, which is marked in the fossil tape by an abundance of marine invertebrates. Maybe the most famous of these invertebrates was the trilobite, an armored arthropod that scuttled around the seafloor for about 270 million years before going extinct.
After the Ordovician Flow came the Silurian Catamenia (443.viii one thousand thousand to 419.2 million years ago), which saw the spread of jawless fish throughout the seas. Mollusks and corals besides thrived in the oceans, merely the big news was what was happening on land: the first undisputed evidence of terrestrial life.
This was the fourth dimension when plants evolved, though they nigh probable did non yet have leaves or the vascular tissue that allows modern plants to siphon upwards water and nutrients. Those developments would appear in the Devonian Period, the next geological period of the Paleozoic. Ferns appeared, as did the offset copse. At the same time, the first vertebrates were colonizing the land. These vertebrates were chosen tetrapods, and they were widely various: Their appearance ranged from lizardlike to snakelike, and their size ranged from four inches (10 cm) long to 16 anxiety (v meters) long, according to a report released in 2009 in the Periodical of Anatomy.
As the tetrapods took over, they had company: The Devonian Menstruation saw the rise of the first state-living arthropods, including the earliest ancestors of spiders.
Paleozoic development
Life continued its march in the late Paleozoic. The Carboniferous Period, which lasted from well-nigh 359 meg years agone to 299 million years ago, answered the question, "Which came first — the chicken or the egg?" definitively. Long before birds evolved, tetrapods began laying eggs on country for the starting time time during this flow, assuasive them to break abroad from an amphibious lifestyle.
Trilobites were fading equally fish became more diverse. The ancestors of conifers appeared, and dragonflies ruled the skies. Tetrapods were becoming more than specialized, and 2 new groups of animals evolved. The first were marine reptiles, including lizards and snakes. The second were the archosaurs, which would requite rise to crocodiles, dinosaurs and birds. Almost creepily, this era is sometimes referred to as the "Age of the Cockroaches," because roaches' ancient ancestor (Archimylacris eggintoni) was found all across the globe during the Carboniferous.
The last menses of the Paleozoic was the Permian Period, which began 298.ix meg years agone and wrapped up 251.9 one thousand thousand years agone. This period would end with the largest mass extinction always: the Permian extinction.
Before the Permian mass extinction, though, the warm seas teemed with life. Coral reefs flourished, providing shelter for fish and shelled creatures, such every bit nautiloids and ammonoids. Modern conifers and ginkgo trees evolved on land. Terrestrial vertebrates evolved to get herbivores, taking reward of the new plant life that had colonized the land.
Paleozoic geology and climate
All this evolution took place confronting the backdrop of shifting continents and a changing climate. During the Cambrian Menstruum of the Paleozoic, the continents underwent a change. They had been joined as one supercontinent, Rodinia, but during the Cambrian Menstruation, Rodinia fragmented into Gondwana (consisting of what would somewhen become the mod continents of the Southern Hemisphere) and smaller continents made up of bits and pieces of the land that would eventually make upwards today's northern continents.
The Cambrian was warm worldwide, but would be followed by an ice age in the Ordovician, which acquired glaciers to form, sending sea levels downward. Gondwana moved further south during the Ordovician, while the smaller continents started to move closer together. In the Silurian Period, the land masses that would become Northward America, primal and northern Europe, and western Europe moved even closer together. Body of water levels rose again, creating shallow inland seas.
In the Devonian, the northern land masses continued merging, and they finally joined together into the supercontinent Euramerica. Gondwana still existed, but the remainder of the planet was bounding main. By the concluding menses of the Paleozoic, the Permian, Euramerica and Gondwana became one, forming peradventure the most famous supercontinent of them all: Pangaea. The giant ocean surrounding Pangaea was chosen Panthalassa. Pangaea'southward interior was likely very dry out, because its massive size prevented h2o-begetting rain clouds from penetrating far across the coasts.
Originally published on Live Scientific discipline.
Source: https://www.livescience.com/37584-paleozoic-era.html
Posted by: winklerwhadminvabot.blogspot.com


0 Response to "During Which Geologic Period Did Plants And Animals First Appear In Land Environments?"
Post a Comment